3.5. Analyse aérodynamique d’une éolienne avec Xfoil#
Marc BUFFAT, département mécanique, UCB Lyon 1

%matplotlib inline
import sympy as sp
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from validation.validation import check_function,bib_validation,exec_validation,info_etudiant
from validation.valide_markdown import test_markdown, test_code, test_algorithme
bib_validation('cours','MGC1061M')
#from Naca import Naca
3.5.1. Xfoil#
XFOIL est un programme pour la conception et l’analyse de profils isolés subsoniques développé au MIT dans les années 90 (https://web.mit.edu/drela/Public/web/xfoil/).
Il permet :
une analyse visqueuse (ou non visqueuse) d’un profil aérodynamique existant avec prise en compte de - transition forcée ou libre - séparation limitée du bord de fuite - correction de compressibilité de Karman-Tsien - nombres de Reynolds et/ou de Mach fixes ou variables
un calcul potentiel (avec une méthode de singularité des panneaux) couplé à un calcul de couche limite
Xfoil est écrit en Fortran 90 et on utilise une bibliothèque Python permettant de l’utiliser directement dans un programme Python.
3.5.1.1. documentation originale#
https://jupyterm1.mecanique.univ-lyon1.fr/cours_html/MGC1061M
from xfoil import XFoil
3.5.1.2. création d’une structure XFoil et définition du profil#
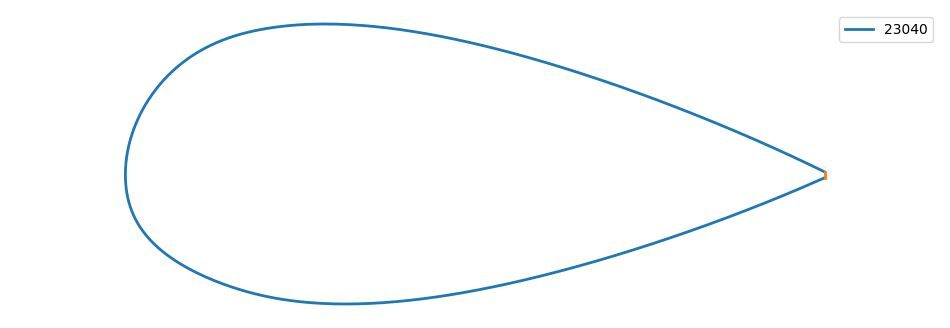
xf = XFoil()
naca_id = "23040"
xf.naca(naca_id)
naca = xf.airfoil
Max thickness = 0.400103 at x = 0.303
Max camber = 0.018385 at x = 0.148
Buffer airfoil set using 425 points
Blunt trailing edge. Gap = 0.00840
Paneling parameters used...
Number of panel nodes 160
Panel bunching parameter 1.000
TE/LE panel density ratio 0.150
Refined-area/LE panel density ratio 0.200
Top side refined area x/c limits 1.000 1.000
Bottom side refined area x/c limits 1.000 1.000
def profil_plot(Xf,Yf,Label=None):
"""trace du profil naca"""
if Label is not None:
plt.plot(Xf,Yf,lw=2,label=Label)
plt.plot([Xf[-1],Xf[0]],[Yf[-1],Yf[0]],lw=2)
else:
plt.plot(Xf,Yf,[Xf[-1],Xf[0]],[Yf[-1],Yf[0]],lw=2)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.axis('off')
return
plt.figure(figsize=(12,4))
profil_plot(naca.x,naca.y,naca_id)
plt.legend();
3.5.1.3. définition des carcatéristiques d’un profil#
étude en fonction de l’angle \(\alpha\)
on spécifie le nombre de Reynolds
\(C_L\) coefficiant de portance: projection suivant \(\vec{N}=[-\sin\alpha, \cos\alpha]\) \(\perp\) à \(\vec{U}_0\)
\(C_m\) coefficient de moment (moment pression) par rapport à un point de référence \(P=[x_{ref}=0.25, y_{ref}=0]\) , qui n’est donc pas nécessairement sur la ligne moyenne à 1/4 de corde
on calcul alors le moment en un point Q quelconque par la relation de transport
d’où la position du centre de poussée exacte / à \(P\) \(x,y\) (erreur)
3.5.1.4. calcul avec xfoil#
toutes les quantités calculées sont adimensionnalisées par la dynamique de l’écoulement amont $\(q = \frac{1}{2} \rho U_0^2 \)\(. Donc un calcul sans dimension assume que le profil est tq \)Lc=1$ (vria pour les profils NACA générés)
Portance \(Cl = L/q\)
trainée \(Cd = D/q\)
moment par rapport au 1/4 corde (xp=0.25, yp=0) \(Cm = M/q\)
calcul pour un angle alpha fixé (en degré)
cl, cd, cm, cp = xf.a(angle)
distribution de pression
xp,Pr = xf.get_cp_distribution()
nombre de Reynolds \(Re=U_0/\nu\) = 0
affichage du calcul
xf.print = True / False
xf.Re = 1.e7
#xf.Re = 0
xf.print = True
cl, cd, cm, cp = xf.a(10)
print("resultat : ",cl,cd,cm,cd)
Calculating unit vorticity distributions ...
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Initializing BL ...
side 1 ...
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 60 Hk = 7.727
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 61 Hk = 2.500
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 93 Hk = 2.500
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 94 Hk = 2.500
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 95 Hk = 2.500
MRCHUE: Convergence failed at 96 side 1 Res = 0.5647E+01
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 97 Hk = 2.500
MRCHUE: Convergence failed at 98 side 1 Res = 0.2763E+02
side 2 ...
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 48 Hk = 2.500
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 63 Hk = 2.500
MRCHUE: Convergence failed at 64 side 2 Res = 0.2442E+02
MRCHUE: Convergence failed at 66 side 2 Res = 0.5781E-01
MRCHDU: Convergence failed at 96 side 1 Res = 0.1845E+01
MRCHDU: Convergence failed at 97 side 1 Res = 0.1848E+01
MRCHDU: Convergence failed at 98 side 1 Res = 0.6353E+02
MRCHDU: Convergence failed at 64 side 2 Res = 0.1856E+01
MRCHDU: Convergence failed at 66 side 2 Res = 0.6215E-01
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1861 60
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5777 49
1 rms: 0.9413E+00 max: 0.5458E+01 D at 66 2 RLX: 0.211
a = 10.000 CL = 1.5533
Cm = -0.0939 CD = 0.00231 => CDf = 0.00511 CDp = -0.00280
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1864 60
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5633 49
2 rms: 0.6081E+00 max: 0.3344E+01 D at 66 2 RLX: 0.359
a = 10.000 CL = 1.4300
Cm = -0.0668 CD = 0.00442 => CDf = 0.00526 CDp = -0.00084
MRCHDU: Convergence failed at 67 side 2 Res = 0.1360E+01
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1867 59
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5576 49
3 rms: 0.7747E+00 max: 0.3610E+01 D at 69 2 RLX: 0.365
a = 10.000 CL = 1.1819
Cm = -0.0244 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00527 CDp = 0.00287
MRCHDU: Convergence failed at 69 side 2 Res = 0.3555E+01
MRCHDU: Convergence failed at 70 side 2 Res = 0.6018E+01
MRCHDU: Convergence failed at 71 side 2 Res = 0.5236E+01
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1869 59
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5482 50
4 rms: 0.3880E+00 max: 0.1903E+01 D at 90 1 RLX: 0.623
a = 10.000 CL = 0.9261
Cm = 0.0227 CD = 0.01527 => CDf = 0.00530 CDp = 0.00998
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2001 58
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5355 52
5 rms: 0.9554E-01 max: 0.7377E+00 D at 86 1
a = 10.000 CL = 0.8050
Cm = 0.0455 CD = 0.02082 => CDf = 0.00487 CDp = 0.01595
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2049 58
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5338 51
6 rms: 0.1301E-01 max: -.1807E+00 D at 86 1
a = 10.000 CL = 0.8172
Cm = 0.0442 CD = 0.02005 => CDf = 0.00474 CDp = 0.01531
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2033 58
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5342 51
7 rms: 0.1730E-01 max: 0.1403E+00 D at 84 1
a = 10.000 CL = 0.8035
Cm = 0.0455 CD = 0.02081 => CDf = 0.00476 CDp = 0.01605
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2034 58
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5340 51
8 rms: 0.6456E-02 max: -.6078E-01 D at 84 1
a = 10.000 CL = 0.8085
Cm = 0.0450 CD = 0.02050 => CDf = 0.00474 CDp = 0.01576
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2034 58
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5341 51
9 rms: 0.1136E-02 max: -.1137E-01 D at 84 1
a = 10.000 CL = 0.8094
Cm = 0.0449 CD = 0.02046 => CDf = 0.00475 CDp = 0.01571
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2034 58
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5341 51
10 rms: 0.7709E-04 max: -.7240E-03 D at 84 1
resultat : 0.8094477653503418 0.020458463579416275 0.04492979869246483 0.020458463579416275
a = 10.000 CL = 0.8094
Cm = 0.0449 CD = 0.02046 => CDf = 0.00475 CDp = 0.01571
9.000 12.9121 0.020458 0.007397 0.000000 -0.007397 0.2034 #
3.5.2. Etude du profil 23020#
xf = XFoil()
naca_id = "23020"
xf.naca(naca_id)
naca = xf.airfoil
X,Y = naca.x, naca.y
Max thickness = 0.200051 at x = 0.303
Max camber = 0.018385 at x = 0.148
Buffer airfoil set using 425 points
Blunt trailing edge. Gap = 0.00420
Paneling parameters used...
Number of panel nodes 160
Panel bunching parameter 1.000
TE/LE panel density ratio 0.150
Refined-area/LE panel density ratio 0.200
Top side refined area x/c limits 1.000 1.000
Bottom side refined area x/c limits 1.000 1.000
3.5.3. Analyse des caractéristiques aero#
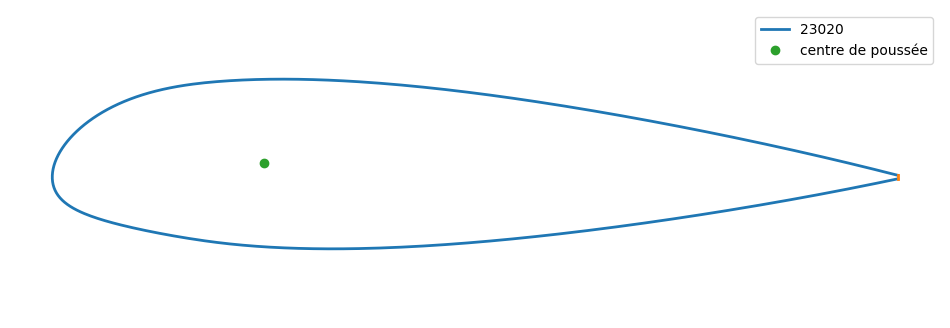
# centre aerodynamique = 1/4 cordre / bord d'attaque
xp = 0.25
I=np.nonzero(np.abs(X-xp)<0.23e-2)[0]
yp = (Y[I].sum())/2.
print("centre aerodynamique :",I,xp,yp)
centre aerodynamique : [128 296] 0.25 0.01651836559176445
plt.figure(figsize=(12,4))
profil_plot(X,Y,"23020")
plt.plot([xp],[yp],'o',label="centre de poussée")
plt.legend();
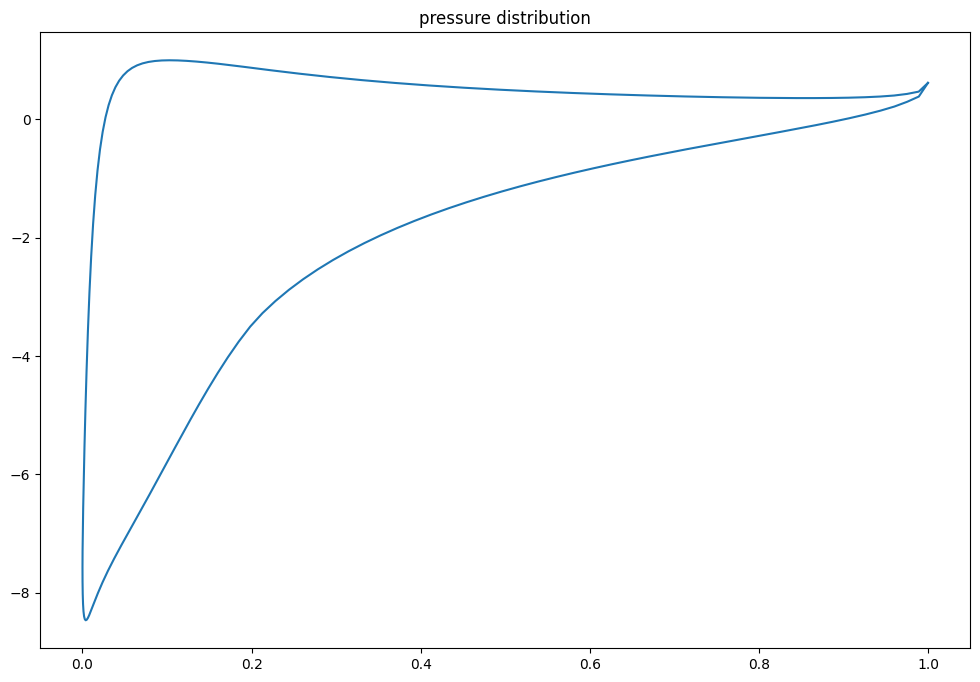
3.5.3.1. portance, moment#
# analyse pour un angle fixe
Alpha=20
Cl, Cd, Cm, Cp = xf.a(Alpha)
print("Angle={} Lift={} Moment={} ".format(Alpha,Cl,Cm))
Xp,Pr = xf.get_cp_distribution()
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.plot(Xp,Pr)
plt.title("pressure distribution")
Calculating unit vorticity distributions ...
Angle=20 Lift=2.654982805252075 Moment=-0.0730389952659607
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'pressure distribution')
# centre de poussée
d = Cm/Cl
print("Position Centre de poussée:",d,xp,xp+d)
Position Centre de poussée: -0.02751015755035222 0.25 0.22248984244964778
3.5.3.2. translation du profil / centre aero#
# translation du profil / au centre de poussé
print("centre de poussée :",xp,yp)
Xt = X - xp
Yt = Y - yp
centre de poussée : 0.25 0.01651836559176445
def trace_profil_rotation(X,Y,theta):
"""trace du profil avec une rotation de theta en degre"""
ca = np.cos(theta*np.pi/180)
sa = np.sin(theta*np.pi/180)
X1 = ca*X + sa*Y
Y1 = -sa*X + ca*Y
plt.plot(X1,Y1)
plt.plot([0],[0],'o')
plt.axis('equal')
return
trace_profil_rotation(Yt,Xt,40)
trace_profil_rotation(Yt,Xt,25)
trace_profil_rotation(Yt,Xt,0)
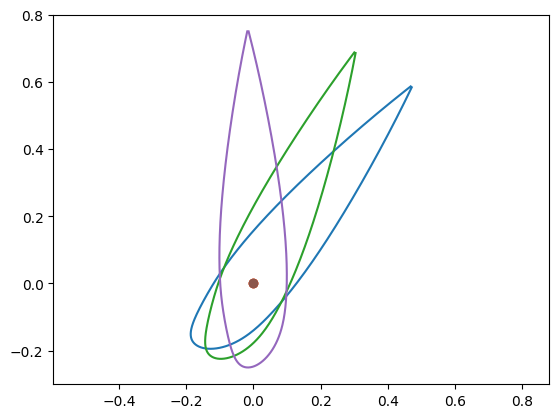
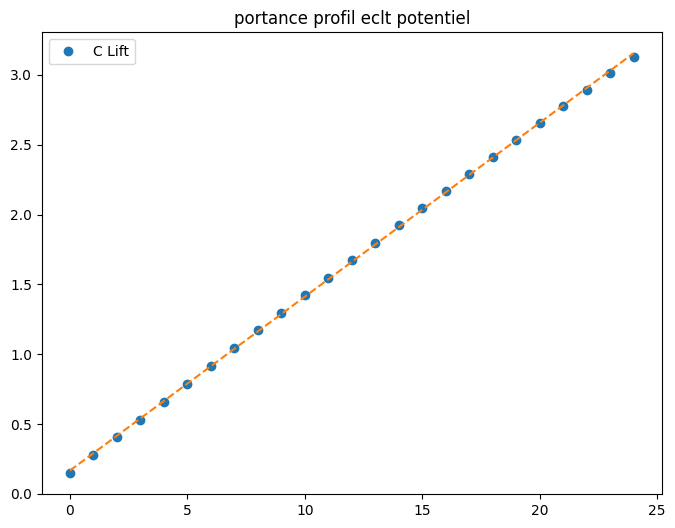
# calcul portance fluide parfait pour # angles
alpha, cl, cd, cm, cp = xf.aseq(0,25,1)
from scipy import stats
a1,a0,r_v,r_p,err = stats.linregress(alpha,cl)
print("loi portance CL= {:.2f}*alpha + {:.2f}".format(a1,a0))
loi portance CL= 0.12*alpha + 0.17
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
plt.plot(alpha,cl,'o',label="C Lift")
plt.plot(alpha,a1*alpha+a0,'--')
plt.title("portance profil eclt potentiel")
plt.legend();
# prise en compte de la viscosite
xf.Re = 1000000
alpha, cl, cd, cm, cp = xf.aseq(0,25,1)
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Initializing BL ...
side 1 ...
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 50 Hk = 4.957
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 51 Hk = 4.580
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 52 Hk = 2.500
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 81 Hk = 2.500
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 82 Hk = 2.500
side 2 ...
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 56 Hk = 4.936
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 57 Hk = 6.218
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 58 Hk = 6.288
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 59 Hk = 2.500
MRCHUE: Inverse mode at 80 Hk = 2.500
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3697 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5556 58
1 rms: 0.2388E+00 max: 0.1249E+01 D at 83 2 RLX: 0.648
a = 0.000 CL = 0.1057
Cm = -0.0030 CD = 0.00690 => CDf = 0.00617 CDp = 0.00072
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3886 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.5778 59
2 rms: 0.6967E-01 max: -.3233E+00 T at 59 2
a = 0.000 CL = 0.1097
Cm = -0.0038 CD = 0.00818 => CDf = 0.00605 CDp = 0.00213
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.4313 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6190 61
3 rms: 0.2660E-01 max: -.4114E+00 C at 54 1
a = 0.000 CL = 0.1172
Cm = -0.0054 CD = 0.00781 => CDf = 0.00560 CDp = 0.00221
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.4207 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6193 61
4 rms: 0.2943E-02 max: 0.4226E-01 C at 61 2
a = 0.000 CL = 0.1160
Cm = -0.0052 CD = 0.00790 => CDf = 0.00556 CDp = 0.00234
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.4191 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6178 61
5 rms: 0.4285E-04 max: -.7058E-03 C at 61 2
a = 0.000 CL = 0.1160
Cm = -0.0052 CD = 0.00790 => CDf = 0.00557 CDp = 0.00233
9.000 3.3757 0.007902 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.4191 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.4191 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6178 61
1 rms: 0.1675E+00 max: 0.1275E+01 C at 54 1 RLX: 0.492
a = 1.000 CL = 0.1686
Cm = -0.0046 CD = 0.00808 => CDf = 0.00557 CDp = 0.00251
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3922 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6343 62
2 rms: 0.7926E-01 max: -.5816E+00 C at 62 2 RLX: 0.860
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2178
Cm = -0.0045 CD = 0.00802 => CDf = 0.00565 CDp = 0.00237
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3688 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6475 62
3 rms: 0.3439E-01 max: -.4154E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2248
Cm = -0.0043 CD = 0.00803 => CDf = 0.00584 CDp = 0.00220
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3675 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6870 63
4 rms: 0.2103E-01 max: -.4007E+00 C at 63 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2223
Cm = -0.0038 CD = 0.00803 => CDf = 0.00562 CDp = 0.00241
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3677 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6673 62
5 rms: 0.3904E-02 max: -.6615E-01 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00568 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6676 62
6 rms: 0.4730E-02 max: -.1063E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
7 rms: 0.4695E-02 max: -.1056E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
8 rms: 0.4700E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
9 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
10 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
11 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
12 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
13 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
14 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
15 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
16 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
17 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
18 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
19 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
20 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
21 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
22 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
23 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
24 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
25 rms: 0.4699E-02 max: -.1057E+00 C at 62 2
a = 1.000 CL = 0.2241
Cm = -0.0042 CD = 0.00814 => CDf = 0.00569 CDp = 0.00246
VISCAL: Convergence failed
9.000 3.4125 0.008142 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.3674 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3674 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.6677 62
1 rms: 0.1521E+00 max: 0.1226E+01 C at 52 1 RLX: 0.865
a = 2.000 CL = 0.3219
Cm = -0.0041 CD = 0.00849 => CDf = 0.00560 CDp = 0.00289
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3248 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.7094 62
2 rms: 0.2288E-01 max: -.1722E+00 D at 52 1
a = 2.000 CL = 0.3318
Cm = -0.0031 CD = 0.00849 => CDf = 0.00580 CDp = 0.00269
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3189 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.7249 63
3 rms: 0.3063E-02 max: 0.5483E-01 C at 63 2
a = 2.000 CL = 0.3303
Cm = -0.0028 CD = 0.00844 => CDf = 0.00572 CDp = 0.00273
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3189 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.7228 63
4 rms: 0.4797E-04 max: -.1022E-02 D at 64 2
a = 2.000 CL = 0.3303
Cm = -0.0028 CD = 0.00845 => CDf = 0.00573 CDp = 0.00272
9.000 3.5416 0.008445 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.3189 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.3189 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.7228 63
1 rms: 0.1647E+00 max: -.1105E+01 D at 52 1 RLX: 0.453
a = 3.000 CL = 0.3770
Cm = -0.0020 CD = 0.00869 => CDf = 0.00567 CDp = 0.00302
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2993 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.7348 63
2 rms: 0.9747E-01 max: -.5606E+00 C at 63 2 RLX: 0.892
a = 3.000 CL = 0.4305
Cm = -0.0019 CD = 0.00882 => CDf = 0.00589 CDp = 0.00293
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2802 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.7888 65
3 rms: 0.1919E-01 max: 0.2758E+00 C at 65 2
a = 3.000 CL = 0.4361
Cm = -0.0015 CD = 0.00887 => CDf = 0.00573 CDp = 0.00314
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2791 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.7771 64
4 rms: 0.1253E-02 max: -.1848E-01 C at 64 2
a = 3.000 CL = 0.4360
Cm = -0.0015 CD = 0.00887 => CDf = 0.00578 CDp = 0.00309
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2788 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.7770 64
5 rms: 0.1343E-04 max: -.2283E-03 D at 51 1
a = 3.000 CL = 0.4360
Cm = -0.0015 CD = 0.00887 => CDf = 0.00578 CDp = 0.00309
9.000 3.8538 0.008874 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.2788 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2788 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.7770 64
1 rms: 0.1501E+00 max: -.7770E+00 D at 51 1 RLX: 0.643
a = 4.000 CL = 0.5033
Cm = -0.0006 CD = 0.00936 => CDf = 0.00571 CDp = 0.00365
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2588 50
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.8085 65
2 rms: 0.5699E-01 max: -.3897E+00 C at 65 2
a = 4.000 CL = 0.5421
Cm = -0.0001 CD = 0.00922 => CDf = 0.00573 CDp = 0.00349
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2531 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.8217 64
3 rms: 0.9260E-02 max: -.1665E+00 C at 64 2
a = 4.000 CL = 0.5424
Cm = -0.0003 CD = 0.00932 => CDf = 0.00581 CDp = 0.00350
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2527 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.8301 65
4 rms: 0.1728E-02 max: -.2545E-01 D at 66 2
a = 4.000 CL = 0.5418
Cm = -0.0001 CD = 0.00929 => CDf = 0.00574 CDp = 0.00355
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2527 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.8289 65
5 rms: 0.3507E-04 max: -.6866E-03 D at 66 2
a = 4.000 CL = 0.5418
Cm = -0.0001 CD = 0.00929 => CDf = 0.00574 CDp = 0.00354
9.000 4.2456 0.009288 0.001261 0.001380 0.000119 0.2527 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2527 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.8288 65
1 rms: 0.1504E+00 max: -.8384E+00 C at 65 2 RLX: 0.596
a = 5.000 CL = 0.6034
Cm = 0.0010 CD = 0.00957 => CDf = 0.00566 CDp = 0.00391
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2417 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.8443 64
2 rms: 0.6003E-01 max: -.3165E+00 T at 64 2
a = 5.000 CL = 0.6487
Cm = 0.0008 CD = 0.00985 => CDf = 0.00585 CDp = 0.00400
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2338 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.8781 66
3 rms: 0.8928E-02 max: 0.1482E+00 C at 66 2
a = 5.000 CL = 0.6457
Cm = 0.0015 CD = 0.00981 => CDf = 0.00570 CDp = 0.00411
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2342 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.8770 66
4 rms: 0.5619E-03 max: 0.1010E-01 C at 66 2
a = 5.000 CL = 0.6457
Cm = 0.0015 CD = 0.00982 => CDf = 0.00570 CDp = 0.00412
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2342 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.8766 66
5 rms: 0.2095E-05 max: -.3138E-04 C at 66 2
a = 5.000 CL = 0.6457
Cm = 0.0015 CD = 0.00982 => CDf = 0.00570 CDp = 0.00411
9.000 4.6032 0.009815 0.001287 0.001463 0.000176 0.2342 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2342 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.8766 66
1 rms: 0.1439E+00 max: -.6258E+00 D at 51 1 RLX: 0.799
a = 6.000 CL = 0.7263
Cm = 0.0032 CD = 0.01037 => CDf = 0.00561 CDp = 0.00476
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2237 51
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9039 66
2 rms: 0.3326E-01 max: -.2440E+00 D at 51 1
a = 6.000 CL = 0.7488
Cm = 0.0033 CD = 0.01035 => CDf = 0.00557 CDp = 0.00477
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2210 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9197 66
3 rms: 0.8447E-02 max: 0.1489E+00 C at 66 2
a = 6.000 CL = 0.7468
Cm = 0.0037 CD = 0.01042 => CDf = 0.00564 CDp = 0.00479
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2206 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9183 66
4 rms: 0.6085E-03 max: -.8757E-02 D at 68 2
a = 6.000 CL = 0.7469
Cm = 0.0037 CD = 0.01043 => CDf = 0.00565 CDp = 0.00478
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2206 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9179 66
5 rms: 0.3810E-05 max: -.5509E-04 C at 66 2
a = 6.000 CL = 0.7469
Cm = 0.0037 CD = 0.01043 => CDf = 0.00565 CDp = 0.00478
9.000 4.8288 0.010426 0.001329 0.001557 0.000228 0.2206 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2206 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9179 66
1 rms: 0.1374E+00 max: 0.4199E+00 D at 66 2
a = 7.000 CL = 0.8450
Cm = 0.0063 CD = 0.01113 => CDf = 0.00556 CDp = 0.00557
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2097 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9480 67
2 rms: 0.2018E-01 max: -.1895E+00 D at 52 1
a = 7.000 CL = 0.8442
Cm = 0.0065 CD = 0.01115 => CDf = 0.00563 CDp = 0.00552
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2094 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9520 67
3 rms: 0.1769E-02 max: 0.1529E-01 C at 52 1
a = 7.000 CL = 0.8432
Cm = 0.0067 CD = 0.01118 => CDf = 0.00562 CDp = 0.00556
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2092 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9527 67
4 rms: 0.2416E-04 max: -.3541E-03 D at 67 2
a = 7.000 CL = 0.8432
Cm = 0.0067 CD = 0.01118 => CDf = 0.00562 CDp = 0.00556
9.000 5.1188 0.011182 0.001377 0.001653 0.000275 0.2092 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.2092 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9527 67
1 rms: 0.1332E+00 max: -.5285E+00 T at 67 2 RLX: 0.946
a = 8.000 CL = 0.9322
Cm = 0.0100 CD = 0.01185 => CDf = 0.00553 CDp = 0.00631
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1989 53
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9776 68
2 rms: 0.2039E-01 max: 0.2371E+00 D at 68 2
a = 8.000 CL = 0.9452
Cm = 0.0078 CD = 0.01230 => CDf = 0.00567 CDp = 0.00663
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1972 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9786 68
3 rms: 0.7513E-02 max: -.9539E-01 D at 52 1
a = 8.000 CL = 0.9455
Cm = 0.0079 CD = 0.01220 => CDf = 0.00566 CDp = 0.00654
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1979 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9783 68
4 rms: 0.1868E-03 max: -.2340E-02 D at 68 2
a = 8.000 CL = 0.9457
Cm = 0.0079 CD = 0.01220 => CDf = 0.00566 CDp = 0.00654
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1979 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9783 68
5 rms: 0.3976E-06 max: -.4245E-05 D at 68 2
a = 8.000 CL = 0.9457
Cm = 0.0079 CD = 0.01220 => CDf = 0.00566 CDp = 0.00654
9.000 5.2443 0.012202 0.001433 0.001760 0.000327 0.1979 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1979 52
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9783 68
1 rms: 0.1515E+00 max: 0.4306E+00 D at 69 2
a = 9.000 CL = 1.0804
Cm = 0.0023 CD = 0.01302 => CDf = 0.00547 CDp = 0.00754
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1888 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9868 66
2 rms: 0.2270E-01 max: -.2789E+00 T at 66 2
a = 9.000 CL = 1.0655
Cm = 0.0050 CD = 0.01325 => CDf = 0.00567 CDp = 0.00758
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1891 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9972 67
3 rms: 0.3567E-01 max: 0.7208E+00 C at 67 2
a = 9.000 CL = 1.0780
Cm = 0.0023 CD = 0.01324 => CDf = 0.00566 CDp = 0.00758
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1887 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9890 66
4 rms: 0.1381E-01 max: -.1611E+00 T at 66 2
a = 9.000 CL = 1.0666
Cm = 0.0047 CD = 0.01325 => CDf = 0.00567 CDp = 0.00758
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1891 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9958 67
5 rms: 0.2673E-01 max: 0.4739E+00 C at 67 2
a = 9.000 CL = 1.0771
Cm = 0.0025 CD = 0.01324 => CDf = 0.00566 CDp = 0.00758
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1887 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9893 67
6 rms: 0.3351E-02 max: -.6850E-01 D at 67 2
a = 9.000 CL = 1.0757
Cm = 0.0027 CD = 0.01327 => CDf = 0.00567 CDp = 0.00759
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1887 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9898 67
7 rms: 0.1995E-04 max: 0.3532E-03 T at 67 2
a = 9.000 CL = 1.0757
Cm = 0.0027 CD = 0.01327 => CDf = 0.00567 CDp = 0.00760
9.000 5.2165 0.013266 0.001509 0.001846 0.000337 0.1887 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1887 54
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9898 67
1 rms: 0.1558E+00 max: 0.2899E+00 D at 67 2 RLX: 0.952
a = 10.000 CL = 1.2048
Cm = -0.0039 CD = 0.01464 => CDf = 0.00546 CDp = 0.00918
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1801 55
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9946 65
2 rms: 0.3303E-01 max: -.3208E+00 D at 55 1
a = 10.000 CL = 1.2091
Cm = -0.0036 CD = 0.01435 => CDf = 0.00564 CDp = 0.00872
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1803 55
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9966 65
3 rms: 0.3214E-02 max: -.3361E-01 D at 56 1
a = 10.000 CL = 1.2082
Cm = -0.0035 CD = 0.01446 => CDf = 0.00565 CDp = 0.00882
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1797 55
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9968 65
4 rms: 0.7887E-04 max: -.8520E-03 D at 56 1
a = 10.000 CL = 1.2082
Cm = -0.0034 CD = 0.01447 => CDf = 0.00565 CDp = 0.00881
9.000 5.3377 0.014466 0.001584 0.001952 0.000368 0.1797 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1797 55
Side 2 free transition at x/c = 0.9968 65
1 rms: 0.1468E+00 max: -.2912E+00 T at 65 2
a = 11.000 CL = 1.3353
Cm = -0.0087 CD = 0.01568 => CDf = 0.00553 CDp = 0.01014
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1709 55
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 64
2 rms: 0.8779E-01 max: -.6506E+00 D at 64 2 RLX: 0.768
a = 11.000 CL = 1.2682
Cm = 0.0039 CD = 0.01577 => CDf = 0.00567 CDp = 0.01011
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1716 55
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 64
3 rms: 0.1250E-01 max: -.1120E+00 C at 64 2
a = 11.000 CL = 1.2558
Cm = 0.0064 CD = 0.01571 => CDf = 0.00567 CDp = 0.01004
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1716 55
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 64
4 rms: 0.2291E-02 max: 0.2557E-01 C at 64 2
a = 11.000 CL = 1.2569
Cm = 0.0062 CD = 0.01571 => CDf = 0.00565 CDp = 0.01006
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1716 55
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 64
5 rms: 0.8530E-04 max: 0.9124E-03 C at 64 2
a = 11.000 CL = 1.2570
Cm = 0.0062 CD = 0.01571 => CDf = 0.00565 CDp = 0.01006
9.000 5.3469 0.015713 0.014192 0.002038 -0.012154 0.1716 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1716 55
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 64
1 rms: 0.1216E+00 max: -.9058E+00 C at 64 2 RLX: 0.552
a = 12.000 CL = 1.2805
Cm = 0.0124 CD = 0.01613 => CDf = 0.00565 CDp = 0.01048
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1694 55
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 64
2 rms: 0.5485E-01 max: 0.9315E-01 D at 69 2
a = 12.000 CL = 1.3153
Cm = 0.0140 CD = 0.01688 => CDf = 0.00545 CDp = 0.01142
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1656 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 63
3 rms: 0.4157E-02 max: -.3642E-01 D at 3 1
a = 12.000 CL = 1.3133
Cm = 0.0141 CD = 0.01695 => CDf = 0.00556 CDp = 0.01140
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1659 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 63
4 rms: 0.2644E-03 max: -.2453E-02 D at 4 1
a = 12.000 CL = 1.3133
Cm = 0.0141 CD = 0.01695 => CDf = 0.00555 CDp = 0.01140
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1659 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 63
5 rms: 0.5679E-06 max: -.5546E-05 C at 63 2
a = 12.000 CL = 1.3133
Cm = 0.0141 CD = 0.01695 => CDf = 0.00555 CDp = 0.01140
9.000 5.3325 0.016952 0.014237 0.002077 -0.012161 0.1659 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1659 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 63
1 rms: 0.1224E+00 max: -.6379E+00 C at 63 2 RLX: 0.784
a = 13.000 CL = 1.3654
Cm = 0.0182 CD = 0.01833 => CDf = 0.00540 CDp = 0.01293
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1602 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 62
2 rms: 0.3564E-01 max: 0.1862E+00 D at 93 1
a = 13.000 CL = 1.3660
Cm = 0.0201 CD = 0.01974 => CDf = 0.00555 CDp = 0.01419
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1576 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 62
3 rms: 0.1911E-01 max: -.1942E+00 D at 56 1
a = 13.000 CL = 1.3752
Cm = 0.0191 CD = 0.01919 => CDf = 0.00550 CDp = 0.01370
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1587 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 62
4 rms: 0.1047E-02 max: 0.7546E-02 T at 56 1
a = 13.000 CL = 1.3759
Cm = 0.0190 CD = 0.01920 => CDf = 0.00549 CDp = 0.01370
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1585 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 62
5 rms: 0.8138E-05 max: -.7775E-04 C at 62 2
a = 13.000 CL = 1.3759
Cm = 0.0190 CD = 0.01920 => CDf = 0.00550 CDp = 0.01370
9.000 6.1693 0.019197 0.014468 0.002156 -0.012312 0.1585 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1585 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 62
1 rms: 0.1217E+00 max: -.3857E+00 C at 62 2
a = 14.000 CL = 1.4531
Cm = 0.0215 CD = 0.02110 => CDf = 0.00533 CDp = 0.01576
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1513 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 61
2 rms: 0.1469E-01 max: 0.1132E+00 D at 92 1
a = 14.000 CL = 1.4424
Cm = 0.0221 CD = 0.02177 => CDf = 0.00543 CDp = 0.01633
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1517 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 61
3 rms: 0.1078E-02 max: 0.2143E-01 D at 91 1
a = 14.000 CL = 1.4421
Cm = 0.0221 CD = 0.02177 => CDf = 0.00540 CDp = 0.01637
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1517 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 61
4 rms: 0.5376E-04 max: -.6008E-03 D at 91 1
a = 14.000 CL = 1.4422
Cm = 0.0221 CD = 0.02177 => CDf = 0.00540 CDp = 0.01637
9.000 6.9961 0.021770 0.014537 0.002198 -0.012339 0.1517 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1517 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 61
1 rms: 0.1245E+00 max: -.4280E+00 D at 57 1 RLX: 0.913
a = 15.000 CL = 1.4942
Cm = 0.0250 CD = 0.02502 => CDf = 0.00522 CDp = 0.01980
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1458 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 60
2 rms: 0.2238E-01 max: -.2125E+00 D at 58 1
a = 15.000 CL = 1.5002
Cm = 0.0247 CD = 0.02524 => CDf = 0.00529 CDp = 0.01996
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1453 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 60
3 rms: 0.1583E-02 max: -.1913E-01 D at 58 1
a = 15.000 CL = 1.4995
Cm = 0.0248 CD = 0.02529 => CDf = 0.00526 CDp = 0.02003
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1450 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 60
4 rms: 0.6143E-04 max: 0.4872E-03 D at 89 1
a = 15.000 CL = 1.4995
Cm = 0.0248 CD = 0.02529 => CDf = 0.00526 CDp = 0.02003
9.000 7.8912 0.025290 0.014532 0.002253 -0.012279 0.1450 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1450 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 60
1 rms: 0.1197E+00 max: 0.3018E+00 D at 88 1 RLX: 0.820
a = 16.000 CL = 1.5492
Cm = 0.0262 CD = 0.02840 => CDf = 0.00507 CDp = 0.02333
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1387 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 59
2 rms: 0.3498E-01 max: 0.2495E+00 D at 89 1
a = 16.000 CL = 1.5392
Cm = 0.0273 CD = 0.03068 => CDf = 0.00522 CDp = 0.02546
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1375 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 59
3 rms: 0.3493E-02 max: 0.4833E-01 D at 88 1
a = 16.000 CL = 1.5402
Cm = 0.0272 CD = 0.03046 => CDf = 0.00516 CDp = 0.02530
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1376 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 59
4 rms: 0.5750E-03 max: -.4572E-02 D at 88 1
a = 16.000 CL = 1.5406
Cm = 0.0272 CD = 0.03043 => CDf = 0.00516 CDp = 0.02527
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1376 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 59
5 rms: 0.2245E-04 max: -.1161E-03 D at 68 2
a = 16.000 CL = 1.5406
Cm = 0.0272 CD = 0.03043 => CDf = 0.00516 CDp = 0.02527
9.000 8.8732 0.030430 0.014363 0.002306 -0.012057 0.1376 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1376 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 59
1 rms: 0.1194E+00 max: -.4784E+00 C at 57 1 RLX: 0.729
a = 17.000 CL = 1.5880
Cm = 0.0275 CD = 0.03327 => CDf = 0.00495 CDp = 0.02832
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1331 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 58
2 rms: 0.3736E-01 max: 0.2068E+00 D at 88 1
a = 17.000 CL = 1.5889
Cm = 0.0279 CD = 0.03576 => CDf = 0.00481 CDp = 0.03095
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1313 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 57
3 rms: 0.6422E-02 max: 0.6786E-01 D at 88 1
a = 17.000 CL = 1.5850
Cm = 0.0280 CD = 0.03590 => CDf = 0.00497 CDp = 0.03093
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1314 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 57
4 rms: 0.8640E-03 max: 0.1138E-01 D at 87 1
a = 17.000 CL = 1.5846
Cm = 0.0281 CD = 0.03590 => CDf = 0.00496 CDp = 0.03095
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1314 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 57
5 rms: 0.4400E-04 max: 0.2114E-03 D at 67 2
a = 17.000 CL = 1.5845
Cm = 0.0281 CD = 0.03590 => CDf = 0.00496 CDp = 0.03094
9.000 9.6797 0.035901 0.014006 0.002316 -0.011690 0.1314 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1314 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 57
1 rms: 0.1253E+00 max: 0.4850E+00 D at 86 1 RLX: 0.623
a = 18.000 CL = 1.6010
Cm = 0.0281 CD = 0.04104 => CDf = 0.00497 CDp = 0.03607
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1273 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 57
2 rms: 0.4546E-01 max: 0.2610E+00 D at 86 1
a = 18.000 CL = 1.6116
Cm = 0.0280 CD = 0.04376 => CDf = 0.00488 CDp = 0.03888
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1248 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 57
3 rms: 0.6209E-02 max: 0.7691E-01 D at 85 1
a = 18.000 CL = 1.6074
Cm = 0.0282 CD = 0.04378 => CDf = 0.00477 CDp = 0.03902
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1248 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 57
4 rms: 0.3115E-03 max: 0.6629E-02 D at 84 1
a = 18.000 CL = 1.6073
Cm = 0.0283 CD = 0.04374 => CDf = 0.00476 CDp = 0.03898
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1248 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 57
5 rms: 0.1679E-04 max: 0.1870E-03 D at 84 1
a = 18.000 CL = 1.6073
Cm = 0.0283 CD = 0.04374 => CDf = 0.00476 CDp = 0.03898
9.000 10.5079 0.043739 0.013501 0.002332 -0.011169 0.1248 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1248 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 57
1 rms: 0.1168E+00 max: 0.4583E+00 D at 83 1 RLX: 0.555
a = 19.000 CL = 1.6219
Cm = 0.0276 CD = 0.04877 => CDf = 0.00453 CDp = 0.04423
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1205 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 56
2 rms: 0.6492E-01 max: 0.4123E+00 D at 84 1
a = 19.000 CL = 1.6107
Cm = 0.0269 CD = 0.05507 => CDf = 0.00469 CDp = 0.05038
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1180 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 56
3 rms: 0.1026E-01 max: 0.1347E+00 D at 83 1
a = 19.000 CL = 1.6060
Cm = 0.0271 CD = 0.05473 => CDf = 0.00458 CDp = 0.05015
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1179 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 56
4 rms: 0.9700E-03 max: 0.2048E-01 D at 82 1
a = 19.000 CL = 1.6059
Cm = 0.0272 CD = 0.05462 => CDf = 0.00456 CDp = 0.05007
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1179 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 56
5 rms: 0.5494E-04 max: 0.2901E-03 D at 82 1
a = 19.000 CL = 1.6059
Cm = 0.0272 CD = 0.05463 => CDf = 0.00456 CDp = 0.05007
9.000 11.3123 0.054626 0.012746 0.002335 -0.010412 0.1179 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1179 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 56
1 rms: 0.1106E+00 max: 0.4353E+00 D at 81 1 RLX: 0.488
a = 20.000 CL = 1.6179
Cm = 0.0260 CD = 0.05957 => CDf = 0.00433 CDp = 0.05524
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1148 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
2 rms: 0.6683E-01 max: 0.3963E+00 D at 82 1
a = 20.000 CL = 1.6098
Cm = 0.0245 CD = 0.06684 => CDf = 0.00444 CDp = 0.06240
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1111 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
3 rms: 0.2112E-01 max: 0.2162E+00 D at 81 1
a = 20.000 CL = 1.5949
Cm = 0.0244 CD = 0.06766 => CDf = 0.00435 CDp = 0.06331
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1115 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
4 rms: 0.3063E-02 max: -.3866E-01 D at 81 1
a = 20.000 CL = 1.5967
Cm = 0.0247 CD = 0.06692 => CDf = 0.00429 CDp = 0.06263
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1115 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
5 rms: 0.2313E-03 max: -.1046E-02 D at 71 2
a = 20.000 CL = 1.5969
Cm = 0.0247 CD = 0.06695 => CDf = 0.00430 CDp = 0.06265
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1115 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
6 rms: 0.7473E-05 max: -.4790E-04 D at 68 2
a = 20.000 CL = 1.5970
Cm = 0.0247 CD = 0.06695 => CDf = 0.00430 CDp = 0.06265
9.000 12.0335 0.066952 0.011879 0.002309 -0.009570 0.1115 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1115 59
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
1 rms: 0.1497E+00 max: 0.8567E+00 D at 79 1 RLX: 0.410
a = 21.000 CL = 1.5786
Cm = 0.0223 CD = 0.07557 => CDf = 0.00431 CDp = 0.07126
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1090 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
2 rms: 0.6713E-01 max: 0.4466E+00 D at 79 1
a = 21.000 CL = 1.5785
Cm = 0.0202 CD = 0.08292 => CDf = 0.00420 CDp = 0.07872
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1047 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
3 rms: 0.1759E-01 max: 0.1875E+00 D at 78 1
a = 21.000 CL = 1.5655
Cm = 0.0204 CD = 0.08288 => CDf = 0.00405 CDp = 0.07884
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1050 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
4 rms: 0.2221E-02 max: -.2764E-01 D at 78 1
a = 21.000 CL = 1.5669
Cm = 0.0206 CD = 0.08224 => CDf = 0.00401 CDp = 0.07823
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1050 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
5 rms: 0.1417E-03 max: -.6892E-03 D at 72 2
a = 21.000 CL = 1.5670
Cm = 0.0205 CD = 0.08226 => CDf = 0.00401 CDp = 0.07824
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1050 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
6 rms: 0.3487E-05 max: -.2577E-04 D at 69 2
a = 21.000 CL = 1.5670
Cm = 0.0205 CD = 0.08226 => CDf = 0.00401 CDp = 0.07825
9.000 12.7908 0.082258 0.010895 0.002282 -0.008613 0.1050 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1050 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
1 rms: 0.1423E+00 max: 0.8649E+00 D at 76 1 RLX: 0.364
a = 22.000 CL = 1.5490
Cm = 0.0178 CD = 0.09084 => CDf = 0.00403 CDp = 0.08682
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.1024 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 55
2 rms: 0.9787E-01 max: 0.7084E+00 D at 76 1
a = 22.000 CL = 1.5080
Cm = 0.0130 CD = 0.10630 => CDf = 0.00371 CDp = 0.10259
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0983 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
3 rms: 0.2024E-01 max: 0.2111E+00 D at 76 1
a = 22.000 CL = 1.5114
Cm = 0.0139 CD = 0.10196 => CDf = 0.00375 CDp = 0.09821
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0986 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
4 rms: 0.5978E-02 max: -.5766E-01 D at 76 1
a = 22.000 CL = 1.5158
Cm = 0.0142 CD = 0.10073 => CDf = 0.00371 CDp = 0.09702
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0983 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
5 rms: 0.5945E-03 max: -.2545E-02 D at 73 2
a = 22.000 CL = 1.5163
Cm = 0.0142 CD = 0.10081 => CDf = 0.00373 CDp = 0.09709
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0983 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
6 rms: 0.3344E-04 max: -.1872E-03 D at 69 2
a = 22.000 CL = 1.5163
Cm = 0.0142 CD = 0.10083 => CDf = 0.00373 CDp = 0.09710
9.000 13.6190 0.100828 0.009799 0.002234 -0.007565 0.0983 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0983 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
1 rms: 0.1358E+00 max: 0.8756E+00 D at 74 1 RLX: 0.324
a = 23.000 CL = 1.4996
Cm = 0.0112 CD = 0.10923 => CDf = 0.00374 CDp = 0.10549
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0958 58
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
2 rms: 0.8198E-01 max: 0.5788E+00 D at 74 1
a = 23.000 CL = 1.4754
Cm = 0.0059 CD = 0.12347 => CDf = 0.00367 CDp = 0.11980
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0915 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
3 rms: 0.2669E-01 max: 0.2943E+00 D at 73 1
a = 23.000 CL = 1.4622
Cm = 0.0055 CD = 0.12196 => CDf = 0.00353 CDp = 0.11843
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0913 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
4 rms: 0.2361E-02 max: -.1924E-01 D at 74 1
a = 23.000 CL = 1.4623
Cm = 0.0058 CD = 0.12063 => CDf = 0.00347 CDp = 0.11717
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0912 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
5 rms: 0.1350E-03 max: 0.1471E-02 D at 72 1
a = 23.000 CL = 1.4623
Cm = 0.0058 CD = 0.12058 => CDf = 0.00347 CDp = 0.11710
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0912 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
6 rms: 0.1228E-04 max: 0.5572E-04 D at 72 1
a = 23.000 CL = 1.4623
Cm = 0.0058 CD = 0.12058 => CDf = 0.00347 CDp = 0.11711
9.000 14.4792 0.120580 0.008773 0.002178 -0.006595 0.0912 #
Calculating wake trajectory ...
Calculating source influence matrix ...
Solving BL system ...
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0912 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
1 rms: 0.1169E+00 max: 0.7716E+00 D at 72 1 RLX: 0.295
a = 24.000 CL = 1.4521
Cm = 0.0028 CD = 0.12774 => CDf = 0.00349 CDp = 0.12426
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0887 57
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
2 rms: 0.8844E-01 max: 0.6119E+00 D at 71 1
a = 24.000 CL = 1.4247
Cm = -0.0047 CD = 0.14527 => CDf = 0.00343 CDp = 0.14184
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0841 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
3 rms: 0.2264E-01 max: 0.2316E+00 D at 71 1
a = 24.000 CL = 1.4168
Cm = -0.0047 CD = 0.14137 => CDf = 0.00330 CDp = 0.13807
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0837 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
4 rms: 0.8188E-02 max: 0.9530E-01 D at 70 1
a = 24.000 CL = 1.4118
Cm = -0.0050 CD = 0.14113 => CDf = 0.00325 CDp = 0.13787
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0836 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
5 rms: 0.1530E-02 max: -.1527E-01 D at 70 1
a = 24.000 CL = 1.4125
Cm = -0.0048 CD = 0.14051 => CDf = 0.00324 CDp = 0.13727
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0836 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
6 rms: 0.1658E-03 max: -.6061E-03 D at 70 1
a = 24.000 CL = 1.4126
Cm = -0.0048 CD = 0.14050 => CDf = 0.00325 CDp = 0.13725
Side 1 free transition at x/c = 0.0836 56
Side 2 forced transition at x/c = 1.0000 54
7 rms: 0.1594E-04 max: -.1009E-03 D at 75 2
a = 24.000 CL = 1.4126
Cm = -0.0048 CD = 0.14051 => CDf = 0.00325 CDp = 0.13727
9.000 15.3326 0.140513 0.007845 0.002119 -0.005726 0.0836 #
# attention resultat
print(alpha)
[ 0. nan 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17.
18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24.]
I = np.isfinite(alpha)
alpha = alpha[I]
cl = cl[I]
cd = cd[I]
cm = cm[I]
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
plt.plot(alpha,cl,'o',label="C Lift")
plt.plot(alpha,cd,'-x',label="C drag")
plt.plot(alpha,a1*alpha+a0,'--',label="Potentiel")
plt.title("portance profil naca")
plt.legend();
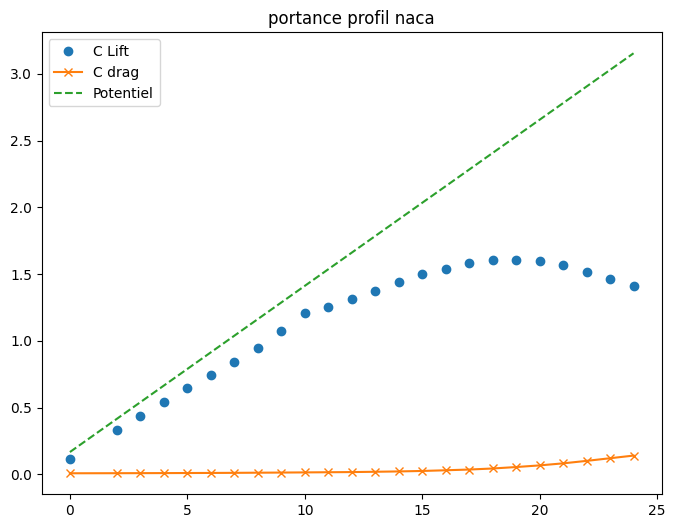
3.5.3.3. Choix du point de fonctionnement#
valeur de l’angle \(\alpha\)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.plot(cd,cl)
plt.title("polaire cl=f(cd)")
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.plot(alpha,cl/cd)
plt.xlabel("$\\alpha$")
plt.title("finesse");
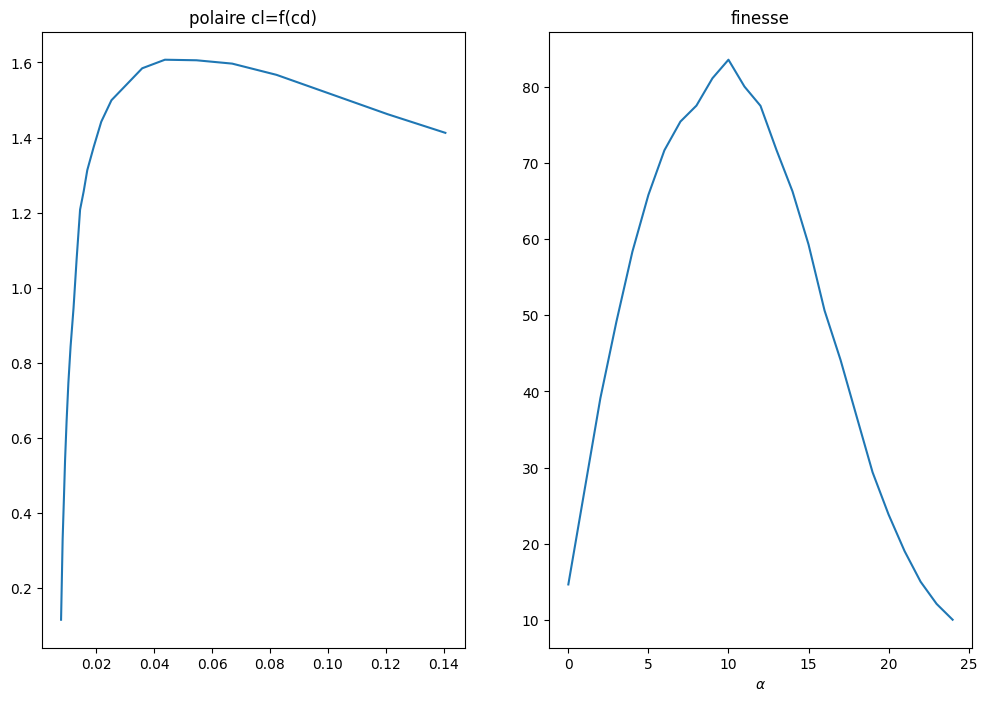
# choix du point de fonctionnement alpha
ALPHA = 12
num=np.where(alpha==ALPHA)[0][0]
print(num,ALPHA)
CD = cd[num]
CL = cl[num]
print("pt fonctionnement ALPHA={} CL={} CD={}".format(ALPHA,CL,CD))
11 12
pt fonctionnement ALPHA=12 CL=1.313344955444336 CD=0.016952097415924072
3.5.4. Etude d’une pale d’eolienne#
étude avec un profil naca 23020
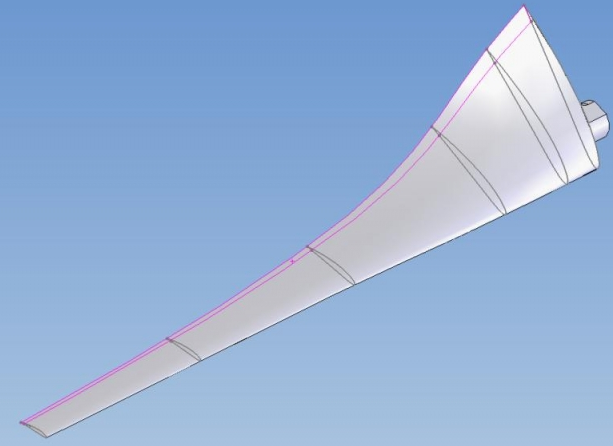
3.5.4.1. caracteristique des pales#
puissance < 200kW
longueur de L= 5 a 20 m
largeur max L/10
rotation max de 400 a 100 tr/mn
rotation omega ~ 20 tr/mn
vrillage de la pale
vitesse optimale du vent V0=15 m/s
vitesse securité < 30 m/s
vitesse minimale 4 m/s
Formule de Betz pour la puissance \(P\): $\( P_{max} = 0.37 S V_0^3 \mbox{ avec } S= \pi L^2 \)$
Modélisation
\(\alpha\) angle d’attaque de la pale
\(\beta\) angle de calage
\(\phi\) angle de la vitesse apparente \(V_a = V_0 - U\)
\(V_0\) vitesse vent
\(U=\omega r\) vitesse de la pale en r
direction tangentielle // à U
direction normale \(\perp\)
\(L\) la portance est \(\perp\) à \(V_a\)
\(L_t\) projection tangentielle de cette force engendrant une rotation de la pale
\(D\) trainée
\(D_t\) projection tangentielle de cette force opposée à la rotation de la pale
\(F_t = L_t -D_t\) résultante (utile) engendrant une puissance \(F_t \omega r\)
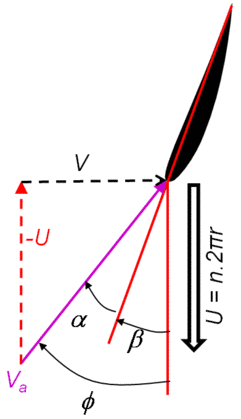
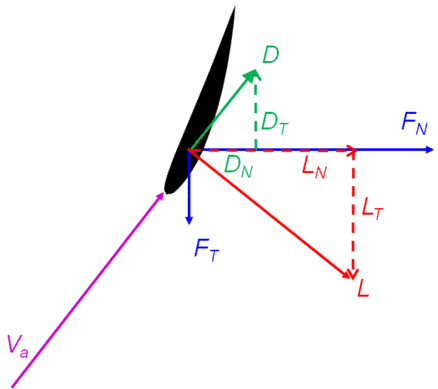
3.5.4.2. Calcul du calage de l’éolienne: analyse dans le plan (t,z)#
t: tangent et z: perpendiculaire au plan de l’éolienne
on veut déterminer \(\beta\) tq l’incidence \(\alpha\) reste constante alors que U varie
r, alpha, omega = sp.symbols('r alpha omega',positive=True)
U0,rho = sp.symbols('U_0 rho',positive=True)
# longueur cordre (l0 en 0 et ~0 pour r = L)
L, l0 = sp.symbols('L l_0',positive=True)
lc = l0*(L-8*r/10)
# angle de calage
U = omega*r
phi = sp.atan2(U0,U)
beta = phi - alpha
beta
angle de calage \(\beta\) tq l’angle d’incidence \(\alpha\) reste contant
# vitesse apparente
Va = sp.sqrt(U0**2+U**2)
Va
# portance et projection suivant la tangente (force utile)
Cp,Cd = sp.symbols('C_p C_d')
P = Cp/2*rho*Va**2*lc
Pt = P*sp.cos(sp.pi/2-phi)
Pt = Pt.simplify()
display("Portance=",Pt)
# trainee
T = Cd*rho/2*Va**2*lc
Tt = -T*sp.cos(phi)
Tt = Tt.simplify()
display("Trainee ",Tt)
'Portance='
'Trainee '
# integration sur la pale pour avoir la force totale utile
FP = sp.integrate(Pt,(r,0,L)) + sp.integrate(Tt,(r,0,L))
FP = FP.simplify()
display("FP=",FP)
'FP='
# puissance totale
PP = sp.integrate(Pt*U,(r,0,L)) + sp.integrate(Tt*U,(r,0,L))
PP = PP.simplify()
display("Puissance totale=",PP)
'Puissance totale='
3.5.5. Valeurs numériques#
# Alpha angle d'incidence en degre, Omega vitesse rotation en tr/min
Alpha=ALPHA
Omega=40.
vals = {sp.pi:np.pi, l0: 1/15. , L:15. , alpha: Alpha*np.pi/180. , omega:Omega*2*np.pi/60.,
U0:15., Cp:CL, Cd:CD, rho:1.0}
print(vals)
# formule Betz
Pmax = 0.37*(rho*sp.pi*L**2*U0**3).subs(vals)/1000
print("(Betz) Pmax={:.1f} kW".format(Pmax))
{pi: 3.141592653589793, l_0: 0.06666666666666667, L: 15.0, alpha: 0.20943951023931953, omega: 4.1887902047863905, U_0: 15.0, C_p: 1.313344955444336, C_d: 0.016952097415924072, rho: 1.0}
(Betz) Pmax=882.7 kW
display("Force totale:",FP)
print("Force portance: {:.2f} N".format(FP.subs(vals)))
print("Puissance totale {:.2f} W".format(3*PP.subs(vals)))
'Force totale:'
Force portance: 2607.91 N
Puissance totale 247985.31 W
# estimation avec formule de Betz
Pmax = 0.37*rho*sp.pi*L**2*U0**3
print("Puissance Betz :",Pmax.subs(vals))
Puissance Betz : 882689.360888307
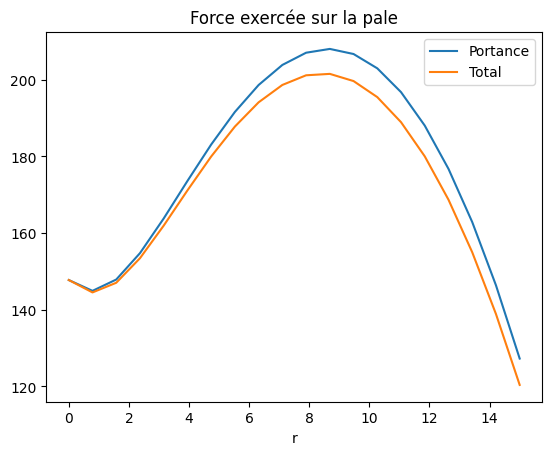
Np = 20
R = np.linspace(0.0,float(L.subs(vals)), Np)
PT = np.array([Pt.subs(vals).subs({r:rr}) for rr in R])
FT = PT + np.array([Tt.subs(vals).subs({r:rr}) for rr in R])
plt.plot(R,PT,label="Portance")
plt.plot(R,FT,label="Total")
plt.title("Force exercée sur la pale")
plt.xlabel("r")
plt.legend();
3.5.5.1. calcul du calage sur 20 secteurs#
Np = 20
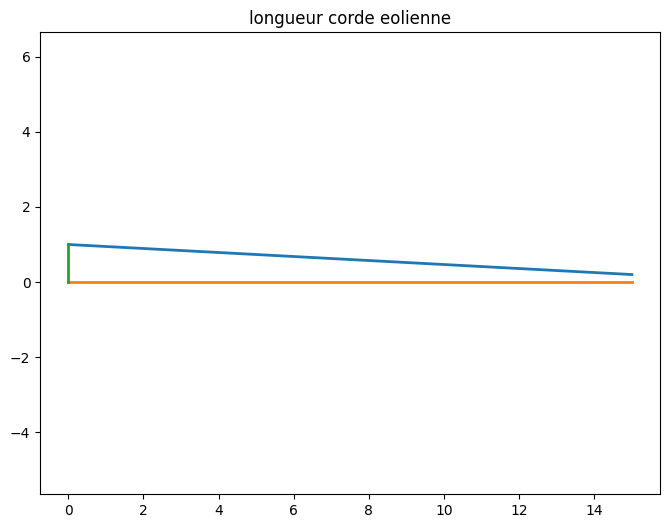
R = np.linspace(0.0,float(L.subs(vals)), Np)
Lc = np.array([lc.subs(vals).subs({r:rr}) for rr in R])
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
plt.plot(R,Lc,lw=2)
plt.plot(R,np.zeros(R.size),lw=2)
plt.plot([0,0],[0,Lc[0]],lw=2)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.title("longueur corde eolienne");
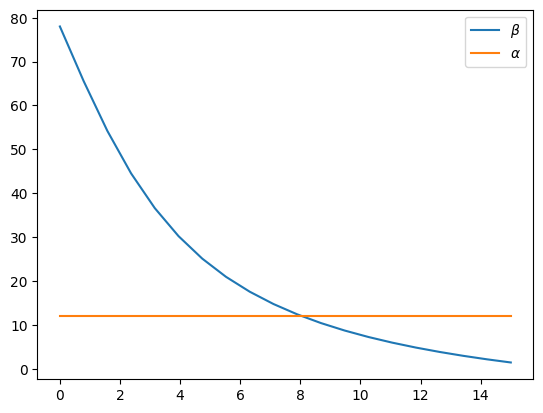
display("beta=",beta)
Beta = np.zeros(Np)
Beta[1:] = np.array([beta.subs(vals).subs({r:rr})*180./np.pi for rr in R[1:]])
Beta[0] = 90. - Alpha
Beta
'beta='
array([78. , 65.56730021, 54.20610468, 44.51983104, 36.59252229,
30.21378638, 25.08876938, 20.94275254, 17.55278074, 14.7476771 ,
12.39864428, 10.40909573, 8.7062407 , 7.23472786, 5.95201274,
4.8250222 , 3.8277544 , 2.93954306, 2.14379171, 1.42704176])
plt.plot(R,Beta,label="$\\beta$")
plt.plot(R,Alpha*np.ones(Np),label="$\\alpha$")
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7fc5659b9750>
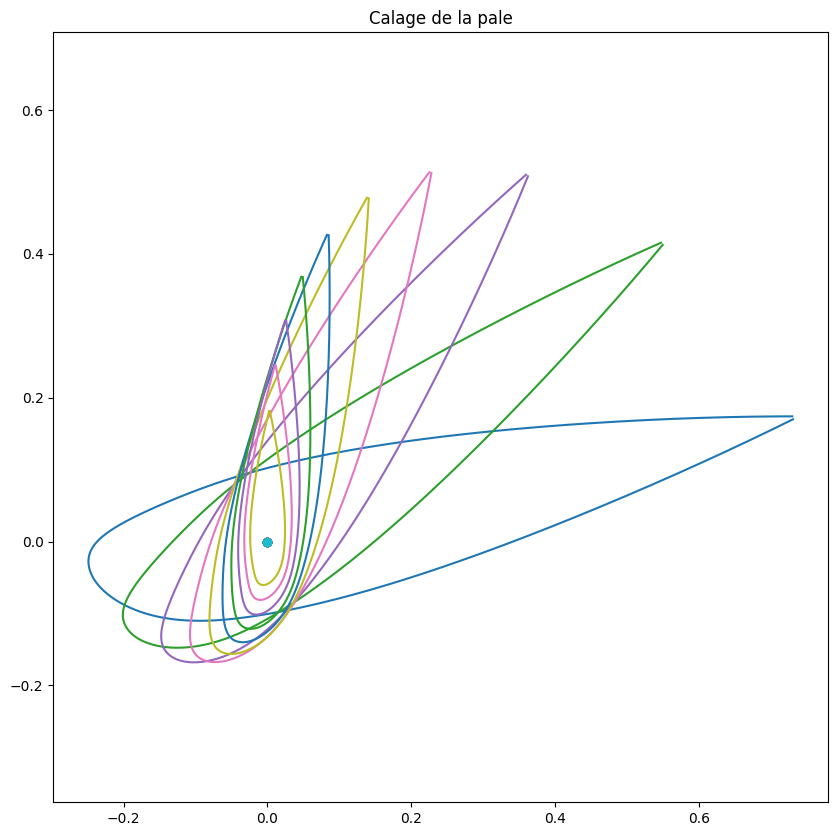
# tracer des profils
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for i in range(0,Np,2):
#print(R[i],Beta[i],Lc[i])
trace_profil_rotation(Yt*Lc[i],Xt*Lc[i],Beta[i])
plt.title("Calage de la pale")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Calage de la pale')
#from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
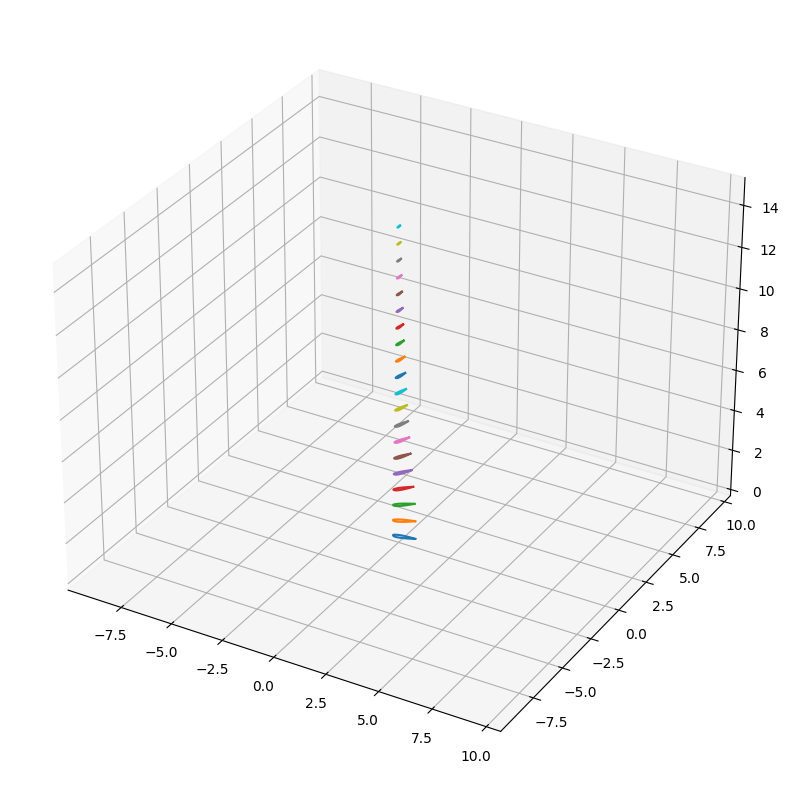
def trace_profil3D(ax,X,Y,Z,theta,lw=2):
ca = np.cos(theta*np.pi/180)
sa = np.sin(theta*np.pi/180)
X1 = ca*X + sa*Y
Y1 = -sa*X + ca*Y
ax.plot(X1, Y1, Z)
return
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
#ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
for i in range(0,Np,1):
#print(i,R[i])
trace_profil3D(ax,Yt[::4]*Lc[i],Xt[::4]*Lc[i],R[i],Beta[i])
#ax.autoscale()
#ax.set_aspect('auto')
plt.axis('equal')
plt.grid()
plt.show()