2. Practical work: Multi-dimensional minimization#
Marc Buffat Dpt mécanique, UCB Lyon 1
%matplotlib inline
#algèbre linéaire
import numpy as np
import sympy as sp
import time
#représentation des résultats
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import display,Markdown
def printmd(text):
display(Markdown(text))
plt.rc('font', family='serif', size='18')
from validation.validation import info_etudiant
def printmd(string):
display(Markdown(string))
# test si numero étudiant spécifier
try: NUMERO_ETUDIANT
except NameError: NUMERO_ETUDIANT = None
if type(NUMERO_ETUDIANT) is not int :
printmd("**ERREUR:** numéro d'étudiant non spécifié!!!")
NOM,PRENOM,NUMERO_ETUDIANT=info_etudiant()
#raise AssertionError("NUMERO_ETUDIANT non défini")
# parametres spécifiques
_uid_ = NUMERO_ETUDIANT
np.random.seed(_uid_)
printmd("**Login étudiant {} {} uid={}**".format(NOM,PRENOM,_uid_))
# fonctionnelle a minimiser
import pwd,sys
libpath=pwd.getpwnam('cours')[5]+'/IntroIA/lib'
sys.path.insert(0, libpath)
from Fonctionnelle import Fonctionnelle
J = Fonctionnelle(_uid_)
printmd("**Fonctionnelle J à minimiser**")
J.info()
ERREUR: numéro d’étudiant non spécifié!!!
Login étudiant Marc BUFFAT uid=137764122
Fonctionnelle J à minimiser
Fonctionnelle J(X)
dimension de X : 43
minimum de J : -1.7692176662626187
pour ||X|| < 1.0
2.1. Objectives#
Find the vector X minimizing the function J(X).
The function J() is written in Python as an object (i.e. a class instance)
J : object name
J.dim() : dimension of X, i.e. number of variables
J(X) : calculate the value of J for a given vector X of dimension J.dim()
J.grad(X) : calculate the gradient of J at X
J.err(X) : calculate the norm of the error ||X-Xe|| where Xe minimize J(X)
J.min() : calculate the minimum of J
2.2. 1D Minimization#
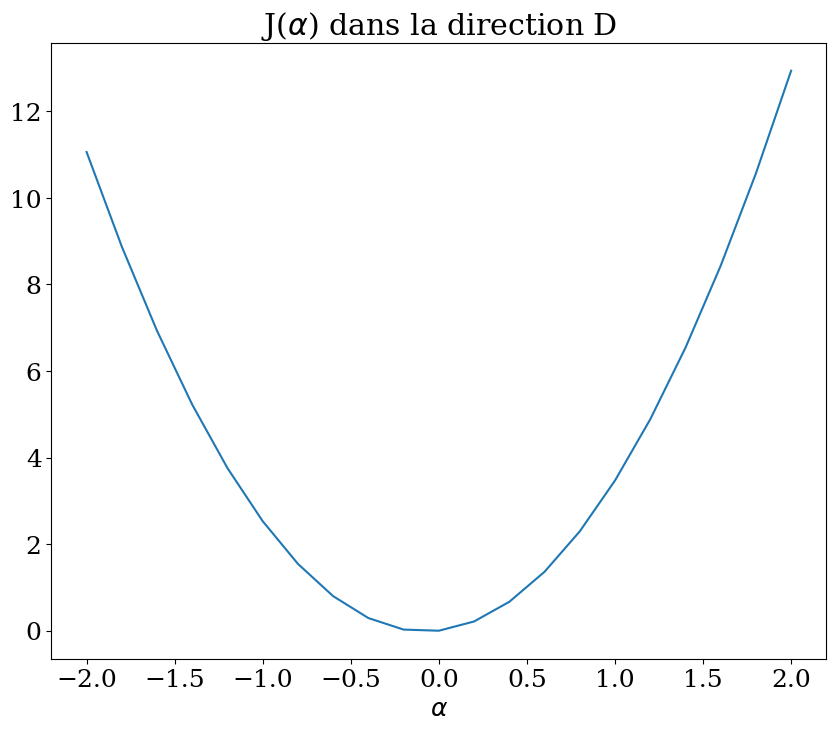
Study of the minimization of \(J(\mathbf{X})\) in a given direction \(\mathbf{D}\)
Given a vector \(D\), we will minimize \(J(\alpha \mathbf{D})\) (as a 1D function of \(\alpha\))
In the following cells:
calculate \(J(\alpha \mathbf{D})\) for different values of \(\alpha\) between -2 and 2
plot the function \(J(\alpha)\)
use the function
minimize_scalarin scipy to calculate \(\alpha\) that minimize \(J(\alpha)\)put the result in the variable
alpha_min
# calcul variation dans une direction D
D = np.zeros(J.dim())
D[NUMERO_ETUDIANT % J.dim()] = 1
Alpha = None
JAlpha = None
### BEGIN SOLUTION
Alpha = np.linspace(-2,2,21)
JAlpha = np.array([J(alpha*D) for alpha in Alpha])
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
plt.plot(Alpha,JAlpha)
plt.xlabel("$\\alpha$")
plt.title("J($\\alpha$) dans la direction D");
### END SOLUTION
from scipy.optimize import minimize_scalar
alpha_min = None
### BEGIN SOLUTION
F = lambda alpha:J(alpha*D)
res = minimize_scalar(F,method='Brent')
print("Jmin=",res.fun)
alpha_min = res.x
print("solution alpha=",alpha_min)
X = alpha_min*D
print("err=",J.err(X))
res
### END SOLUTION
Jmin= -0.018356381667365942
solution alpha= -0.07822271977579136
err= 1.3365604110647604
message:
Optimization terminated successfully;
The returned value satisfies the termination criteria
(using xtol = 1.48e-08 )
success: True
fun: -0.018356381667365942
x: -0.07822271977579136
nit: 5
nfev: 8
print(f"alpha={alpha_min} minimise J suivant D\n",D)
assert(J.err1D(alpha_min,D)<1.e-5)
alpha=-0.07822271977579136 minimise J suivant D
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
2.3. multi-dimensional minimization#
use of the scipy library
function minimize (local minimization)
method using exact gradient : Conjugate Gradients, Newton GC,
méthod using approximate gradient : BFGS,
line search Powell, Simplex Nelder-Mead
global optimization
simulated annealing
In the following cell, define 2 new functions :
F(X) to calculate J(X)
Fgrad(X) to calculate the gradient
we use python functions because the minimization function does not allow class method.
F = None
Fgrad = None
### BEGIN SOLUTION
F = lambda X:J(X)
Fgrad = lambda X:J.grad(X)
### END SOLUTION
X0 = np.zeros(J.dim())
print("solution initiale X0:\n",X0)
assert np.allclose(F(X0),J(X0))
assert np.allclose(Fgrad(X0),J.grad(X0))
solution initiale X0:
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
2.3.1. Using the default minimize method#
for each method, we have too:
calculate the solution Xe,
calculate the value of J(Xe)
calculate the error (that should be less than 1.e-5)
We have to prescribe the optional parameters in order to obtain the prescribed precision
from scipy.optimize import minimize
Xe = None
### BEGIN SOLUTION
res = minimize(F, X0,options={'disp':True})
Xe = res.x
print("Jmin=",res.fun,res.message)
print('solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:\n',Xe)
print("Erreur = ",J.err(Xe))
### END SOLUTION
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: -1.769218
Iterations: 26
Function evaluations: 1892
Gradient evaluations: 43
Jmin= -1.7692176662297645 Optimization terminated successfully.
solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:
[ 0.37669914 0.0473201 -0.05940651 0.24743475 0.10194773 0.04459198
0.20554939 0.02195719 0.0379892 0.44592214 0.54024204 0.29085524
-0.11742665 0.17566061 0.13499798 0.10380401 -0.12442166 0.27601026
-0.22541101 0.07267743 0.12516503 0.27537963 0.19022756 0.0380975
0.21712647 -0.00406927 0.07766843 -0.1020846 -0.01725833 0.08505746
-0.07205854 0.15775652 0.06561638 0.11190708 -0.06764155 0.45226144
-0.05877664 0.03460216 0.02844345 0.08316676 0.20954806 0.02630892
0.464114 ]
Erreur = 6.022753004989829e-06
print(f"J={J(Xe)} avec erreur={J.err(Xe)} pour X:\n",Xe)
assert( J.err(Xe) < 1.e-5)
J=-1.7692176662297645 avec erreur=6.022753004989829e-06 pour X:
[ 0.37669914 0.0473201 -0.05940651 0.24743475 0.10194773 0.04459198
0.20554939 0.02195719 0.0379892 0.44592214 0.54024204 0.29085524
-0.11742665 0.17566061 0.13499798 0.10380401 -0.12442166 0.27601026
-0.22541101 0.07267743 0.12516503 0.27537963 0.19022756 0.0380975
0.21712647 -0.00406927 0.07766843 -0.1020846 -0.01725833 0.08505746
-0.07205854 0.15775652 0.06561638 0.11190708 -0.06764155 0.45226144
-0.05877664 0.03460216 0.02844345 0.08316676 0.20954806 0.02630892
0.464114 ]
2.3.2. Conjugate gradient Method#
Xe = None
### BEGIN SOLUTION
res = minimize(F, X0, jac=Fgrad, method='CG',options={'disp':True})
print("Jmin=",res.fun,res.message)
Xe = res.x
print('solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:\n',Xe)
print("Erreur = ",J.err(Xe))
### END SOLUTION
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: -1.769218
Iterations: 20
Function evaluations: 41
Gradient evaluations: 41
Jmin= -1.7692176662297676 Optimization terminated successfully.
solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:
[ 0.37669861 0.04732022 -0.05940598 0.24743562 0.1019499 0.04459283
0.20555072 0.02195744 0.03799154 0.44592203 0.54024449 0.2908546
-0.11742708 0.17566174 0.13500079 0.10380474 -0.12442238 0.27600939
-0.22540979 0.07267734 0.12516579 0.2753805 0.19023037 0.03809888
0.21712764 -0.00406822 0.07766976 -0.10208394 -0.01725912 0.08505799
-0.07205764 0.15775932 0.06561639 0.11191097 -0.06764046 0.45226228
-0.05877647 0.03460051 0.02844238 0.08316826 0.20954934 0.02630826
0.46411377]
Erreur = 4.636842973251503e-06
print(f"J={J(Xe)} avec erreur={J.err(Xe)} pour X:\n",Xe)
assert( J.err(Xe) < 1.e-5)
J=-1.7692176662297676 avec erreur=4.636842973251503e-06 pour X:
[ 0.37669861 0.04732022 -0.05940598 0.24743562 0.1019499 0.04459283
0.20555072 0.02195744 0.03799154 0.44592203 0.54024449 0.2908546
-0.11742708 0.17566174 0.13500079 0.10380474 -0.12442238 0.27600939
-0.22540979 0.07267734 0.12516579 0.2753805 0.19023037 0.03809888
0.21712764 -0.00406822 0.07766976 -0.10208394 -0.01725912 0.08505799
-0.07205764 0.15775932 0.06561639 0.11191097 -0.06764046 0.45226228
-0.05877647 0.03460051 0.02844238 0.08316826 0.20954934 0.02630826
0.46411377]
2.3.3. Conjugate gradient Method with Newton#
Xe = None
### BEGIN SOLUTION
res = minimize(F, X0, jac=Fgrad, method='Newton-CG',options={'disp':True})
print("Jmin=",res.fun,res.message)
Xe = res.x
print('solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:\n',Xe)
print("Erreur = ",J.err(Xe))
### END SOLUTION
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: -1.769218
Iterations: 9
Function evaluations: 10
Gradient evaluations: 77
Hessian evaluations: 0
Jmin= -1.7692176662626165 Optimization terminated successfully.
solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:
[ 0.37670016 0.04732056 -0.05940647 0.24743543 0.10194923 0.04459226
0.20555026 0.02195688 0.03799023 0.44592269 0.54024409 0.29085522
-0.11742721 0.1756614 0.13499967 0.10380462 -0.12442221 0.27600989
-0.22541077 0.07267732 0.12516558 0.27537939 0.19022893 0.03809801
0.2171283 -0.00406866 0.0776689 -0.10208422 -0.01725887 0.08505769
-0.07205837 0.1577582 0.06561628 0.11190963 -0.06764064 0.45226276
-0.05877668 0.03460125 0.02844297 0.08316746 0.2095486 0.02630885
0.46411378]
Erreur = 5.184269262151714e-08
print(f"J={J(Xe)} avec erreur={J.err(Xe)} pour X:\n",Xe)
assert( J.err(Xe) < 1.e-5)
J=-1.7692176662626165 avec erreur=5.184269262151714e-08 pour X:
[ 0.37670016 0.04732056 -0.05940647 0.24743543 0.10194923 0.04459226
0.20555026 0.02195688 0.03799023 0.44592269 0.54024409 0.29085522
-0.11742721 0.1756614 0.13499967 0.10380462 -0.12442221 0.27600989
-0.22541077 0.07267732 0.12516558 0.27537939 0.19022893 0.03809801
0.2171283 -0.00406866 0.0776689 -0.10208422 -0.01725887 0.08505769
-0.07205837 0.1577582 0.06561628 0.11190963 -0.06764064 0.45226276
-0.05877668 0.03460125 0.02844297 0.08316746 0.2095486 0.02630885
0.46411378]
2.3.4. Method BFGS (use of a numerical approximation of the gradient)#
Xe = None
### BEGIN SOLUTION
res = minimize(F, X0, method='BFGS',options={'disp':True})
print("Jmin=",res.fun,res.message)
Xe = res.x
print('solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:\n',Xe)
print("Erreur = ",J.err(Xe))
### END SOLUTION
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: -1.769218
Iterations: 26
Function evaluations: 1892
Gradient evaluations: 43
Jmin= -1.7692176662297645 Optimization terminated successfully.
solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:
[ 0.37669914 0.0473201 -0.05940651 0.24743475 0.10194773 0.04459198
0.20554939 0.02195719 0.0379892 0.44592214 0.54024204 0.29085524
-0.11742665 0.17566061 0.13499798 0.10380401 -0.12442166 0.27601026
-0.22541101 0.07267743 0.12516503 0.27537963 0.19022756 0.0380975
0.21712647 -0.00406927 0.07766843 -0.1020846 -0.01725833 0.08505746
-0.07205854 0.15775652 0.06561638 0.11190708 -0.06764155 0.45226144
-0.05877664 0.03460216 0.02844345 0.08316676 0.20954806 0.02630892
0.464114 ]
Erreur = 6.022753004989829e-06
print(f"J={J(Xe)} avec erreur={J.err(Xe)} pour X:\n",Xe)
assert( J.err(Xe) < 1.e-5)
J=-1.7692176662297645 avec erreur=6.022753004989829e-06 pour X:
[ 0.37669914 0.0473201 -0.05940651 0.24743475 0.10194773 0.04459198
0.20554939 0.02195719 0.0379892 0.44592214 0.54024204 0.29085524
-0.11742665 0.17566061 0.13499798 0.10380401 -0.12442166 0.27601026
-0.22541101 0.07267743 0.12516503 0.27537963 0.19022756 0.0380975
0.21712647 -0.00406927 0.07766843 -0.1020846 -0.01725833 0.08505746
-0.07205854 0.15775652 0.06561638 0.11190708 -0.06764155 0.45226144
-0.05877664 0.03460216 0.02844345 0.08316676 0.20954806 0.02630892
0.464114 ]
2.3.5. Powell Algorithm (line search 2D)#
Xe = None
### BEGIN SOLUTION
res = minimize(F, X0, method='Powell',options={'disp':True,'xtol':1.e-8,'ftol':1.0e-8})
print("Jmin=",res.fun,res.message)
Xe = res.x
print('solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:\n',Xe)
print("Erreur = ",J.err(Xe))
### END SOLUTION
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: -1.769218
Iterations: 15
Function evaluations: 11097
Jmin= -1.7692176530299948 Optimization terminated successfully.
solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:
[ 0.37667005 0.04731831 -0.0594059 0.24742969 0.10194837 0.04459097
0.20554676 0.02193932 0.03799056 0.44591172 0.540236 0.29083952
-0.11742493 0.175661 0.13499505 0.10380322 -0.12441626 0.27598852
-0.2254106 0.07267111 0.12514853 0.27537008 0.19022729 0.03809785
0.21702824 -0.00405411 0.07766853 -0.10208704 -0.0172583 0.08506079
-0.07205901 0.15775171 0.06562448 0.11185635 -0.06764132 0.45225323
-0.05878437 0.03459999 0.02842351 0.0831695 0.20954474 0.02630869
0.46409637]
Erreur = 0.00012918732312904748
print(f"J={J(Xe)} avec erreur={J.err(Xe)} pour X:\n",Xe)
assert( J.err(Xe) < 1.e-3)
J=-1.7692176530299948 avec erreur=0.00012918732312904748 pour X:
[ 0.37667005 0.04731831 -0.0594059 0.24742969 0.10194837 0.04459097
0.20554676 0.02193932 0.03799056 0.44591172 0.540236 0.29083952
-0.11742493 0.175661 0.13499505 0.10380322 -0.12441626 0.27598852
-0.2254106 0.07267111 0.12514853 0.27537008 0.19022729 0.03809785
0.21702824 -0.00405411 0.07766853 -0.10208704 -0.0172583 0.08506079
-0.07205901 0.15775171 0.06562448 0.11185635 -0.06764132 0.45225323
-0.05878437 0.03459999 0.02842351 0.0831695 0.20954474 0.02630869
0.46409637]
2.3.6. Simulated annealing#
from scipy.optimize import dual_annealing
Xe = None
### BEGIN SOLUTION
bounds = [[-1,1]]*J.dim()
res=dual_annealing(F,bounds=bounds)
print(res)
print("Jmin=",res.fun,res.message)
Xe = res.x
print('solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:\n',Xe)
print("Erreur = ",J.err(Xe))
### END SOLUTION
message: ['Maximum number of iteration reached']
success: True
status: 0
fun: -1.7692176657187755
x: [ 3.767e-01 4.732e-02 ... 2.631e-02 4.641e-01]
nit: 1000
nfev: 87101
njev: 25
nhev: 0
Jmin= -1.7692176657187755 ['Maximum number of iteration reached']
solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:
[ 0.37669304 0.04731865 -0.05940457 0.24743587 0.1019486 0.04459476
0.20555101 0.02195361 0.03799474 0.44591705 0.54023352 0.29085377
-0.11742663 0.17565963 0.13499311 0.10380461 -0.12442111 0.27600705
-0.22540478 0.07267668 0.1251646 0.27537906 0.1902271 0.03809665
0.21711575 -0.00407089 0.0776704 -0.10208516 -0.01725787 0.08505986
-0.07205864 0.15775122 0.0656194 0.11189518 -0.06764063 0.45225393
-0.05877729 0.03459876 0.02843693 0.08316774 0.20955133 0.02630694
0.46411592]
Erreur = 3.0295365921744437e-05
print(f"J={J(Xe)} avec erreur={J.err(Xe)} pour X:\n",Xe)
assert( J.err(Xe) < 1.e-4)
J=-1.7692176657187755 avec erreur=3.0295365921744437e-05 pour X:
[ 0.37669304 0.04731865 -0.05940457 0.24743587 0.1019486 0.04459476
0.20555101 0.02195361 0.03799474 0.44591705 0.54023352 0.29085377
-0.11742663 0.17565963 0.13499311 0.10380461 -0.12442111 0.27600705
-0.22540478 0.07267668 0.1251646 0.27537906 0.1902271 0.03809665
0.21711575 -0.00407089 0.0776704 -0.10208516 -0.01725787 0.08505986
-0.07205864 0.15775122 0.0656194 0.11189518 -0.06764063 0.45225393
-0.05877729 0.03459876 0.02843693 0.08316774 0.20955133 0.02630694
0.46411592]
2.3.7. Simplex Method (Nelder-Mead)#
Xe = None
### BEGIN SOLUTION
bounds = [[-1,1]]*J.dim()
res = minimize(F, X0, method='Nelder-Mead',bounds=bounds,
options={'disp':True, 'maxiter':500000,
'fatol':1.0e-5,'xatol':1.0e-5})
print("Jmin=",res.fun,res.message)
Xe = res.x
print('solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:\n',Xe)
print("Erreur = ",J.err(Xe))
# non cvge
### END SOLUTION
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: -1.200344
Iterations: 50200
Function evaluations: 57706
Jmin= -1.2003442377984364 Optimization terminated successfully.
solution J(Xe)={J(Xe)} pour Xe:
[ 0.06226151 -0.01369773 -0.08780471 0.17376409 -0.02158641 -0.01399093
0.12676538 -0.03677043 0.0391837 0.01440498 0.18608908 0.14652088
-0.16919761 0.08411006 -0.05828204 0.05404556 -0.1838678 0.14468501
-0.2567649 -0.01107447 0.15114776 0.27385515 0.07086723 -0.00843397
-0.06355823 -0.07906294 0.00129312 -0.19059111 -0.09705945 0.04175389
-0.14878703 0.04611975 -0.04325124 -0.09645403 -0.11890353 -0.02834005
-0.05615334 -0.06193063 -0.07806562 0.00308665 0.07942687 -0.042194
0.23473536]
Erreur = 1.0398428044675592
print(f"J={J(Xe)} avec erreur={J.err(Xe)} pour X:\n",Xe)
#assert( J.err(Xe) < 0.8)
J=-1.2003442377984364 avec erreur=1.0398428044675592 pour X:
[ 0.06226151 -0.01369773 -0.08780471 0.17376409 -0.02158641 -0.01399093
0.12676538 -0.03677043 0.0391837 0.01440498 0.18608908 0.14652088
-0.16919761 0.08411006 -0.05828204 0.05404556 -0.1838678 0.14468501
-0.2567649 -0.01107447 0.15114776 0.27385515 0.07086723 -0.00843397
-0.06355823 -0.07906294 0.00129312 -0.19059111 -0.09705945 0.04175389
-0.14878703 0.04611975 -0.04325124 -0.09645403 -0.11890353 -0.02834005
-0.05615334 -0.06193063 -0.07806562 0.00308665 0.07942687 -0.042194
0.23473536]
2.4. Analysis#
comparison of the different methods
computational cost
precision
Write your analysis using Markdown syntax
